Stablecoins backed by LSTs
An In-depth Look into CDPs in LSTfi, and overcollateralized crypto backed stablecoins
Intro
Stablecoins are among the most proven use cases of cryptocurrency in an environment where a large portion of the world wishes to avoid the restrictions of the US banking system while still having access to a USD-denominated currency. Stablecoins like Tether (USDT) are incredibly useful, with daily trading volumes in the billions. However, users often depend heavily on banking infrastructure and trust in the custodian's practices is paramount. This is where stablecoins backed by crypto assets and now LSTs (Liquid Staking Tokens) come in.
This research paper highlights key innovations in the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, focusing on collateralized debt positions in liquid staking Defi (LSTfi). Key players within the LST-backed CDP sectors, such as crvUSD, Lybra, Raft, Gravita, and Dinero, emerge as first movers in the growing landscape, utilizing unique protocols mechanics to enable financial stability and capital efficiency within the DeFi ecosystem. This study aims to provide insights to help evaluate the potential risks and benefits associated with these rapidly evolving protocols.
Stablecoin Trilemma
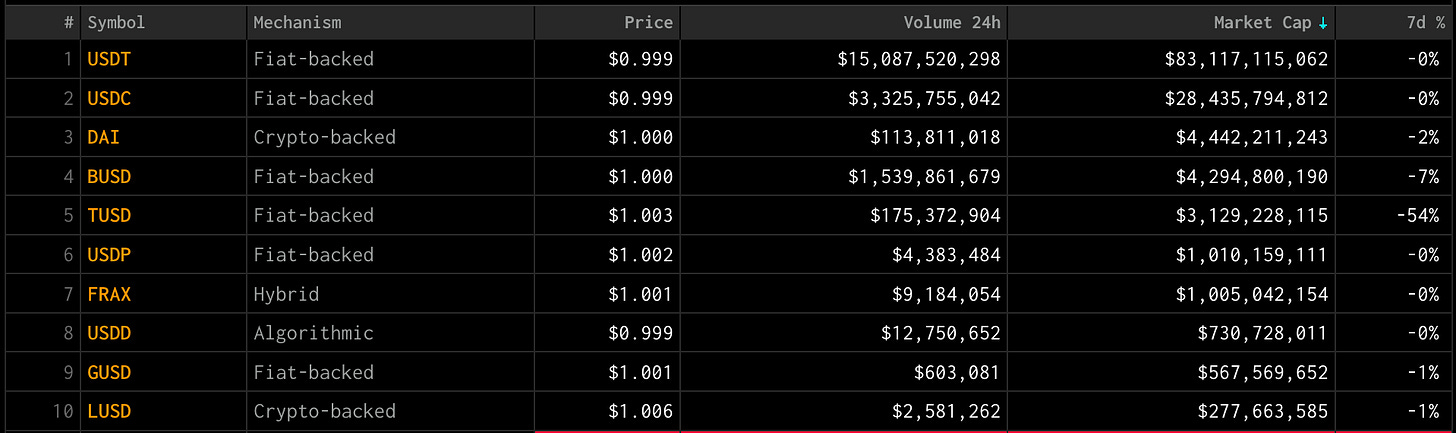
Stablecoins, though varied in design, are universally aimed at maintaining a stable value, typically pegged to the USD. Two of the top five cryptocurrencies by market capitalization are stablecoins, predominantly backed by USD or US Treasuries. Despite the large on-chain volumes commanded by USDC (USD Coin) and USDT (Tether), the market seeks alternatives, primarily due to these stablecoins' reliance on off-chain trust.
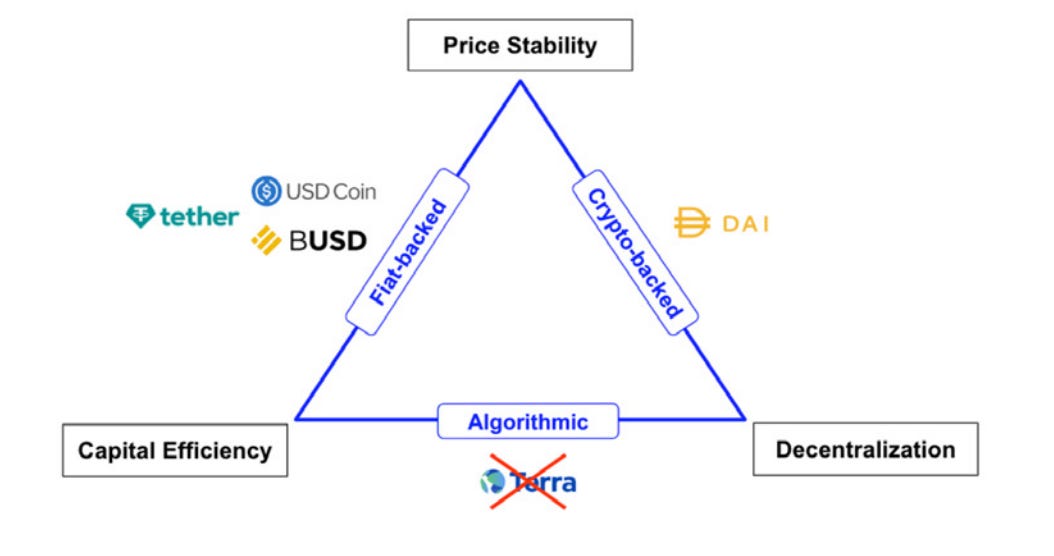
Designing a stablecoin involves a complex problem, the so-called stablecoin trilemma, which envisions an ideal stablecoin as having three core attributes: price stability, decentralization, and capital efficiency.
Price stability: Maintaining a stable peg.
Decentralization: distributing powers and governance away from a central authority.
Capital Efficiency: Effective utilization of resources to generate maximum output or returns. Prevention of idle money.
The leading fiat-backed stablecoins offer capital efficiency and price stability but fall short in decentralization. While these have become the default stablecoins for many market participants, due to increasing regulatory scrutiny and transparency issues, users have begun exploring diverse stablecoin models. Algorithmic stablecoins, which are capital efficient and decentralized, are one such option, although they may face a potential "death spiral," as observed with Terra Luna’s UST.
The third architecture, crypto-backed stables, combines decentralization and price stability but falls short in capital efficiency. The permissionless nature of crypto and decentralized markets largely drive the crypto ethos. However, many market participants, especially newcomers and institutional actors, do not put decentralization high on their list of priorities. This lack of emphasis, along with first-mover advantages, fuels the explosive growth in fiat-backed stables. The early market entry of fiat-backed USDT also played a significant role in spurring the surge of fiat-backed stablecoins. Consequently, crypto-backed stablecoins have not emerged as the top preference for many.
LST-backed stablecoins interrogate this trilemma in an effort to bridge all three components, creating a reliable medium of exchange.
Collateralized Debt Position - CDP
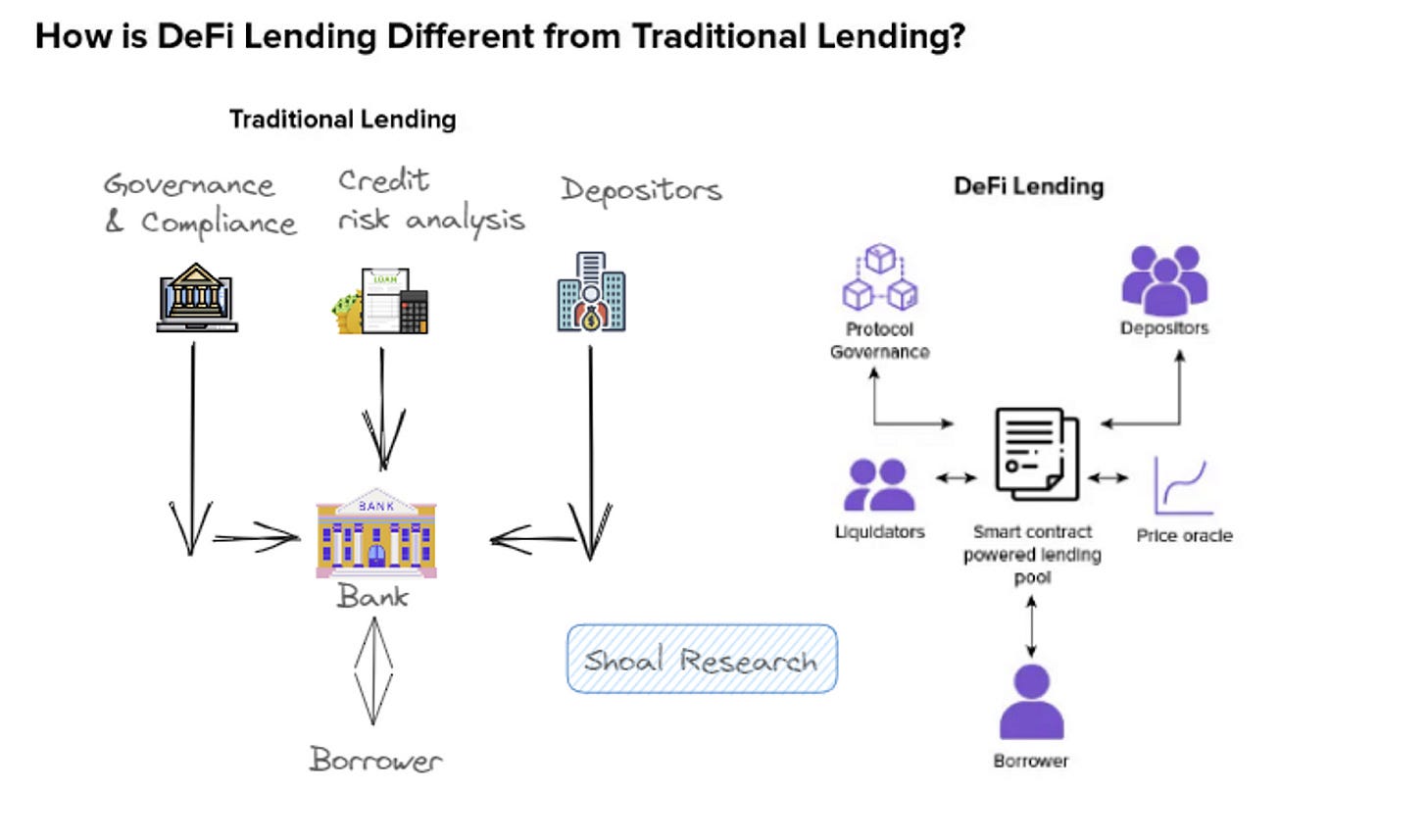
In traditional finance, there exists a concept known as collateralized debt obligations (CDOs). These financial instruments are essentially bundles of loans or other valuable assets that can be utilized to offset losses if a loan repayment fails. Despite their inherent risk, they are considered practical tools in the financial sector since they grant depositors a line of credit backed by their assets.
With the advent of blockchain technology, similar structures emerge without the need for banks or intermediaries. Collateralized debt positions, known as CDPs, are permissionless assets backed by on-chain deposits of other assets. Akin to digital vaults, users can deposit valuable digital assets, such as Ethereum (ETH), and in exchange, they receive another digital token, often a stablecoin like DAI. Stablecoins are useful because they are engineered to maintain a stable value close to $1, thus enabling users to have access to a less volatile asset (DAI) for payments while still maintaining exposure to the underlying asset (ETH).
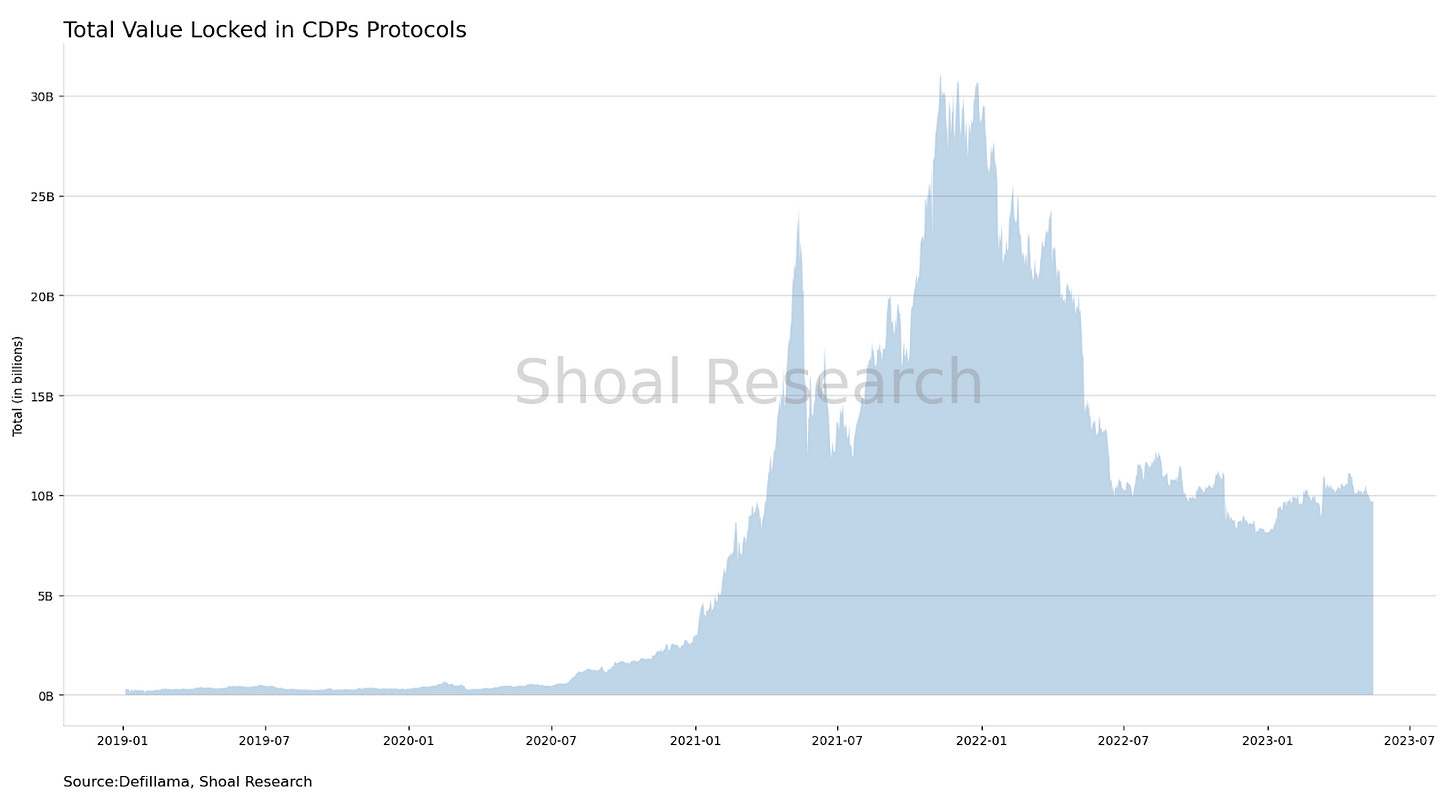
There are over forty such systems, collectively valued at over $8.9 billion. The largest among these is MakerDAO, which holds more than $7.6 billion in assets.
LSTfi
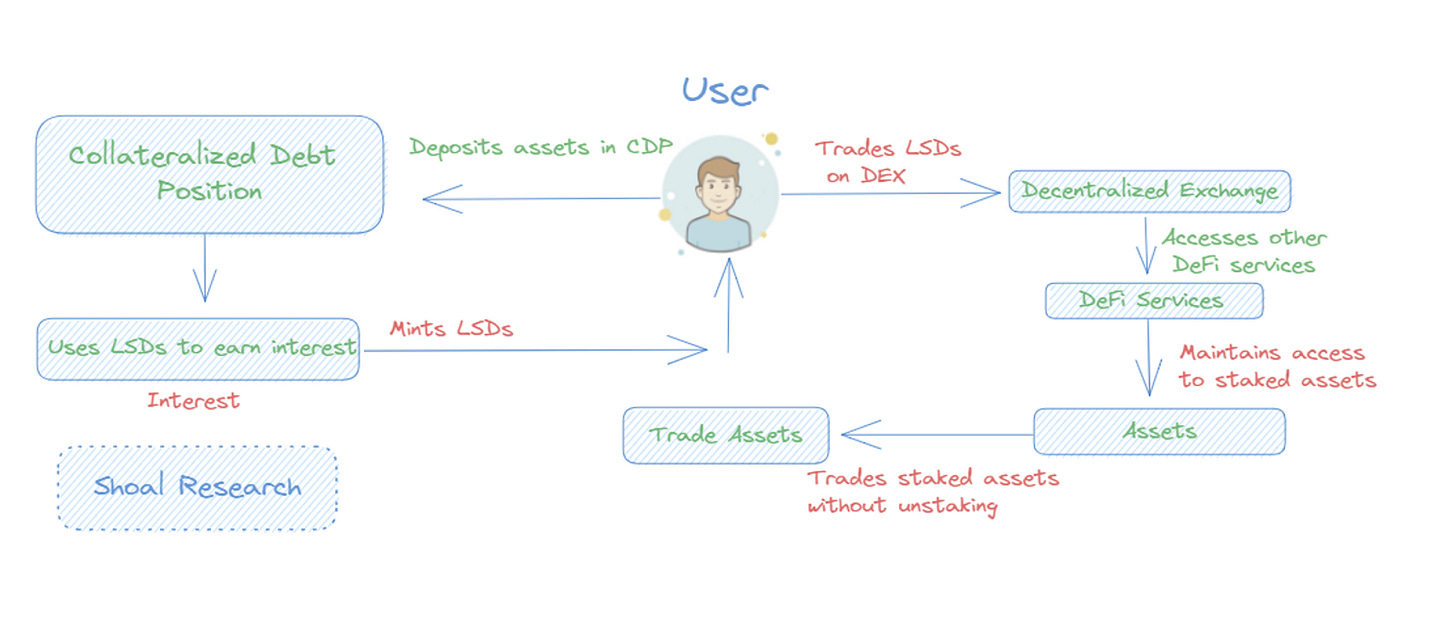
Liquid Staking Derivatives Finance (LSTfi) comprises decentralized finance protocols that extensively utilize Liquid staking tokens (LSTs) in DeFi operations. LSTs are typically ERC-20 tokens representing a user's staked ETH, such as stETH issued by Lido. With LSTs, users can earn rewards, trade on decentralized exchanges, and utilize other DeFi services. The primary advantages of LSTfi include the capability for users to earn interest on their staked assets while maintaining access to them and the opportunity to trade staked assets without needing to unstake them.
CDPs in LSTfi
Currently, there is a huge race among CDP protocols competing within LSTfi to capture TVL (total locked value). The CDP LSDfi protocols follow the same general principles where users can deposit their staked assets to mint stablecoins. In the context of LSTfi, users typically deposit a LST (stETH) to borrow a stablecoin (like R, raft stablecoin) against it (as shown in the Figure below). If the value of a user's collateral falls below a certain threshold, their assets will be liquidated (sold off) to cover the decrease in prices, resulting in the loss of their staked assets. Here are the benefits of using CDPs:
Earn interest on staked assets: Users can earn interest on their staked assets by minting LSDs and using them to yield earnings on DeFi protocols.
Trade-staked assets without unstaking: Users can trade staked assets without having to unstake them by using LSDs. This can benefit users who want to seize market opportunities without needing to tie up their stakes.
Access DeFi services: Users can access DeFi services, such as lending and borrowing, by using LSDs. This is useful for those who want to use their staking assets to generate income or hedge against market volatility.
The emergence of LSTfi protocols has been driven by the desire for more stable and less volatile financial instruments within the cryptocurrency market. These protocols often offer unique features and benefits, such as lower liquidation risk, and yield farming opportunities, giving market participants more utilities for assets they already own.
At the time of writing, approximately $18.34 billion is locked in liquid staking protocols, and around $9.37 billion is locked in DeFi CDP protocols. This is in comparison to the all-time high of $30.5 billion locked in CDPs during the peak of the 2021 bull market, largely driven by MakerDao.
These emerging protocols, each with unique offerings and associated projects are shaping the future of LSTfi with CDPs. Here are some of the notable ones:
crvUSD: A stablecoin that rebalances user collateral into more stable assets as the price falls, thus reducing liquidation risk.
Lybra: Known for eUSD, a yield-producing stablecoin.
Raft: Single collateral stETH and smart liquidation through flash mints.
Gravita: Borrower-friendly terms and focus on censorship resistance.
Dinero: Upcoming LSTfi protocol that will leverage its LST for stablecoin minting
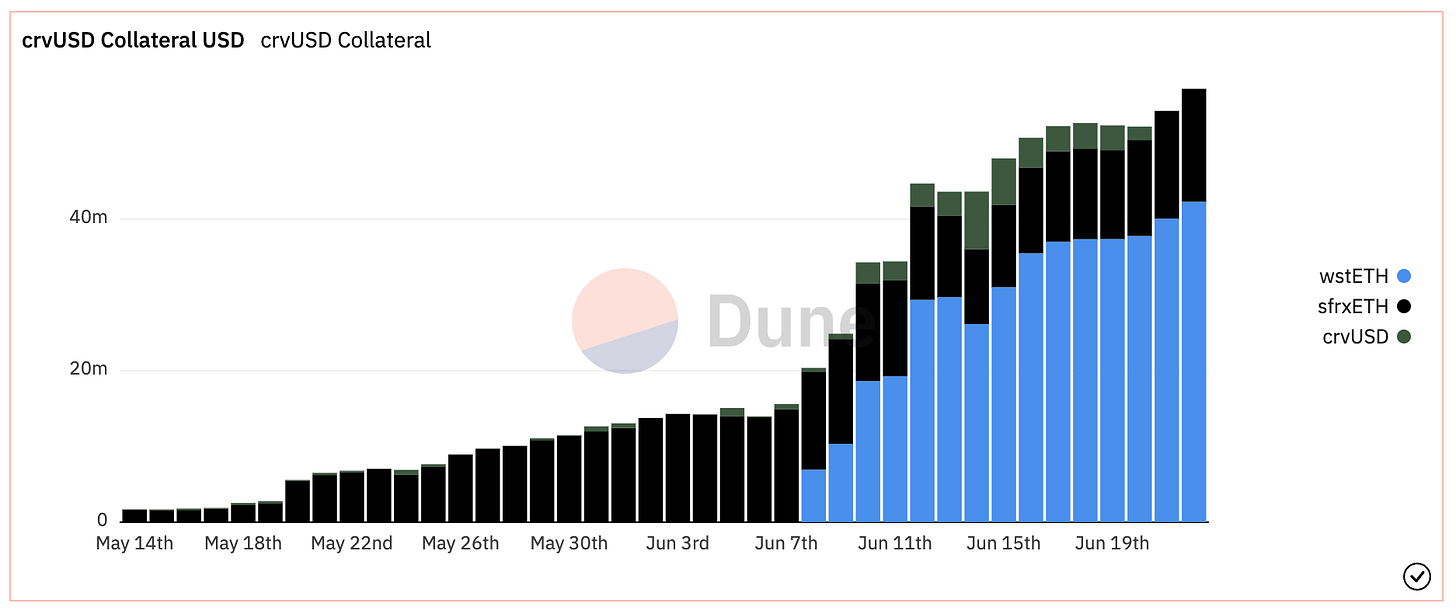
crvUSD
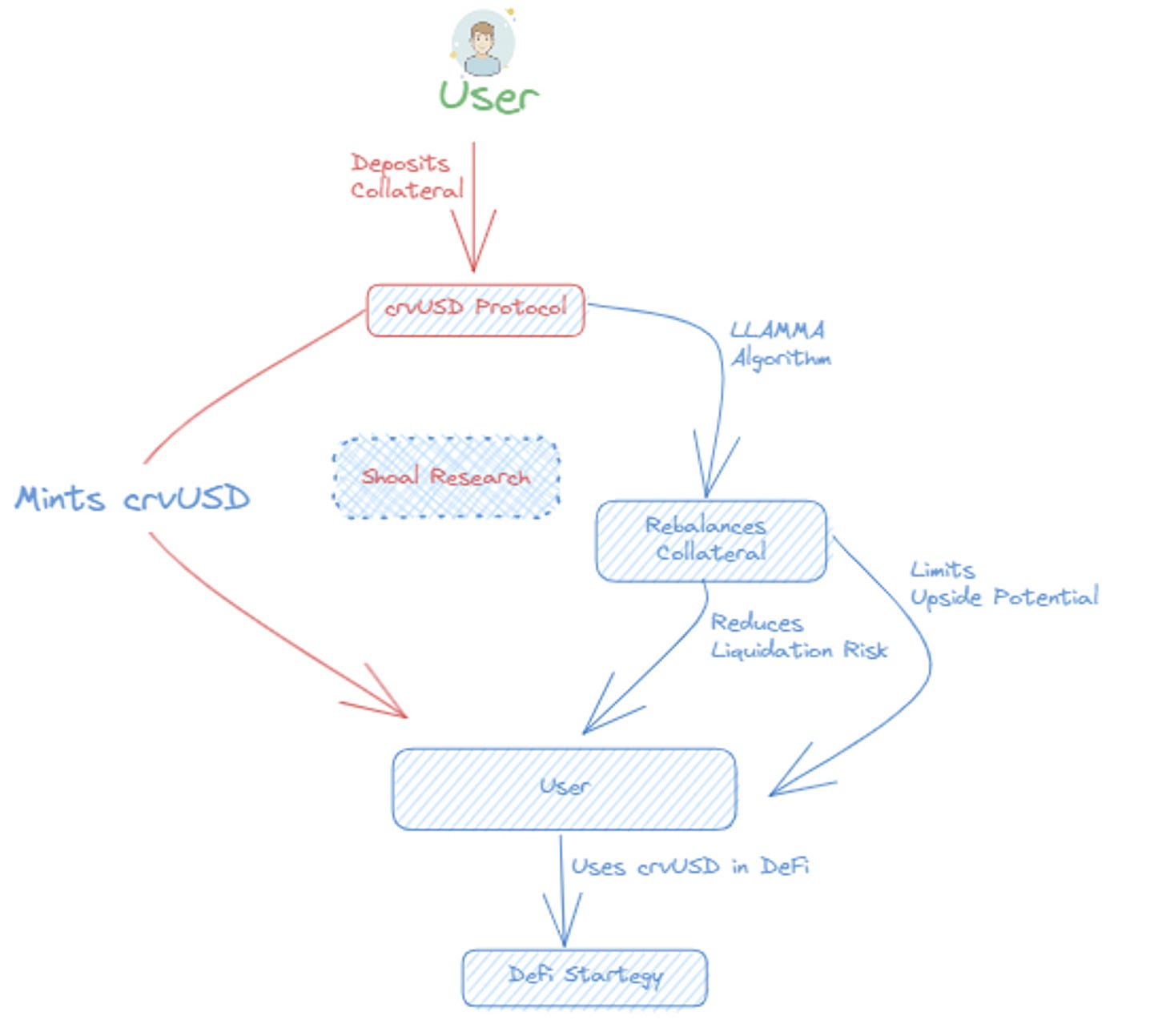
CrvUSD is a decentralized stablecoin launched by Curve Finance, a DeFi protocol known for optimizing swaps between identically pegged digital assets, primarily stablecoins. Users deposit collateral to take out a loan in CrvUSD. Initially, CrvUSD will likely accept ETH as collateral, similar to DAI by MakerDAO. Eventually, Liquidity Pool (LP) positions might also be accepted as collateral options. Unlike most CDPs, crvUSD automatically rebalances users' collateral into more stable assets as the price falls, which reduces liquidation risk but potentially limits upside gains.
The liquidation mechanism is possible through the lending-liquidating AMM algorithm (LLAMMA). This algorithm sets specific price bands to liquidate portions of the collateral rather than fully liquidating it at a specific price. As the price of the collateral falls, it is sold for CrvUSD. When the collateral value hits the targeted liquidation point, there will already be enough CrvUSD to cover the loan value, averting a typical liquidation scenario. Conversely, as the price of the collateral recovers, crvUSD is converted back into the posted collateral.
This mechanism of crvUSD could attract more liquidity providers to Curve's LPs, thereby achieving greater capital efficiency with their funds. Coupled with the reduced risk of liquidations thanks to LLAMMA, this could be very enticing for risk-averse users looking to incorporate elements of leverage into their DeFi strategy.
Lybra Protocol
Lybra is a DeFi protocol that introduces eUSD, the first interest-bearing stablecoin. The protocol operates on a collateralized debt position (CDP) mechanism, where users deposit ETH or STETH as collateral to mint eUSD. The stability of eUSD is maintained through a combination of over-collateralization, liquidation mechanisms, and arbitrage opportunities.
Lybra's unique interest-bearing stablecoin, eUSD, generates a base annual percentage yield (APY). This stable yield attracts users seeking a steady income stream while maintaining exposure to ETH staking. Furthermore, as the price of ETH increases, the yield generated by eUSD holders also rises, and conversely, it decreases in the event of a price drop.
Zero Minting Fees and Loan Interest
Lybra differentiates itself from other stablecoin protocols by offering users zero minting fees and zero loan interest. This feature allows users to leverage their ETH holdings and mint eUSD stablecoins without incurring additional costs.
How Lybra Works
Deposit: Users deposit ETH or stETH as collateral.
Mint eUSD: Users can mint or borrow eUSD against their collateral.
Receive Interest or Spend: Users can hold eUSD to receive interest APY or use it in other DeFi protocols.
Raft Protocol
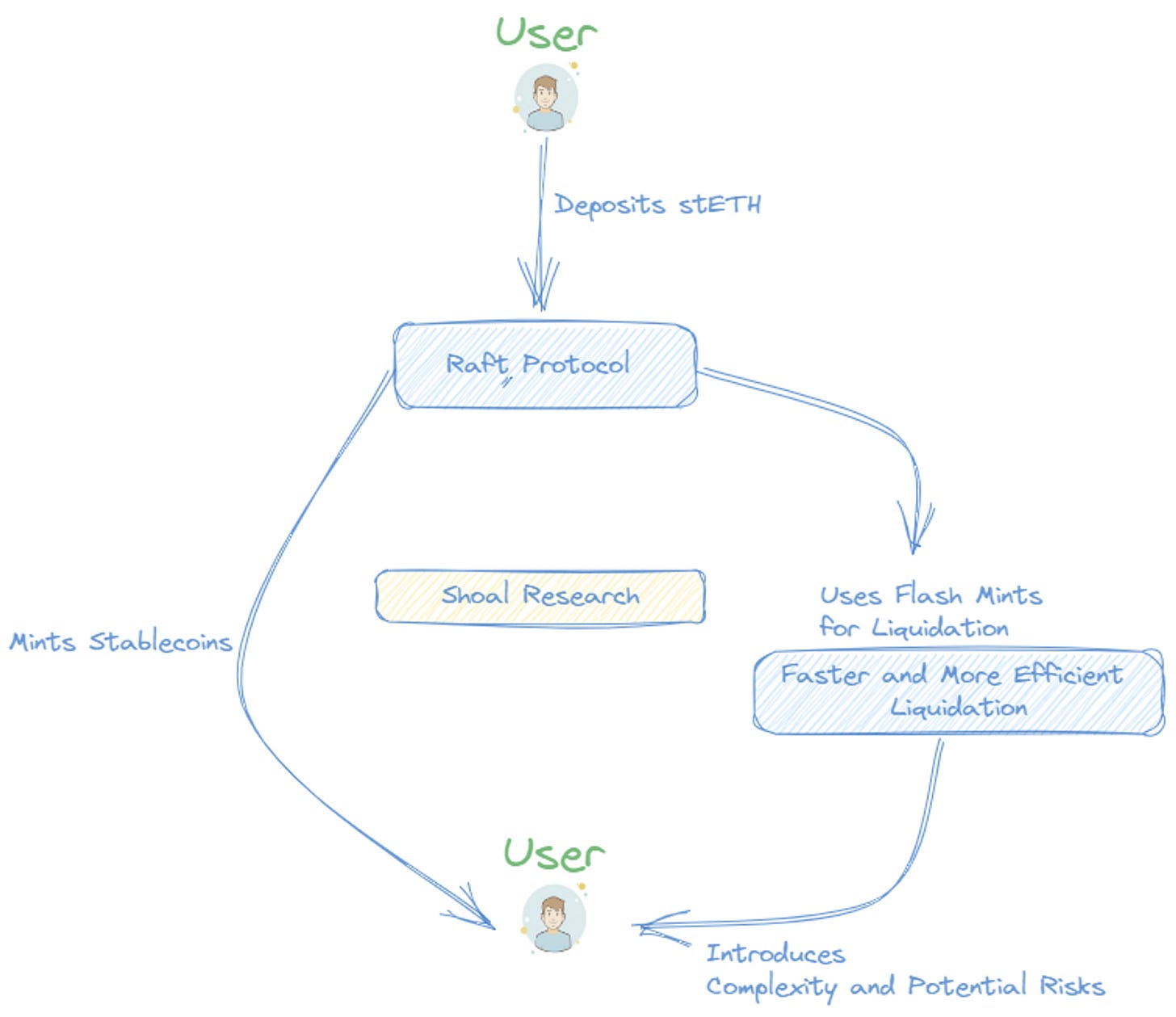
Raft is the first US dollar stablecoin collateralized solely by Lido Staked Ether (stETH). This stablecoin is designed to retain a value of 1 USD, maintaining its peg through a combination of hard peg and soft peg mechanisms.
The launch of Raft provides a solution for Lido users seeking capital-efficient ways to use their stETH. The protocol allows depositors to generate R, a decentralized USD stablecoin, using their stETH, eliminating the need for fiat backing. On a positive note, Raft's Total Value Locked (TVL) jumped to $29 million in just three days, representing a daily increase of 15%.
One-Step Leverage
One of the unique features that Raft plans to introduce soon is one-step leverage, which enables users to trade with up to 11x leverage on stETH in a single transaction. This leverage ratio is higher than what any other platform currently offers. Moreover, Raft simplifies the complex multi-step transactions required to gain leverage on stETH through other loan platforms like Aave or Maker. This functionality utilizes Flash Mint to offer leverage on stETH.
Raft Flash mints
Another unique feature of Raft is its use of flash mints rather than a stability pool for liquidation. A flash mint is a type of flash loan, a feature offered by some DeFi protocols that allow users to borrow and repay an asset within the same transaction. This can be used for various purposes, including arbitrage, collateral swapping, and self-liquidation. Using flash mints for liquidation aims to make the liquidation process faster and more efficient. However, it also introduces additional complexity and potential risks.
Gravita
The Gravita Protocol is a unique, Ethereum-based borrowing system offering interest-free loans using liquid staking tokens (LSTs) and a stability pool (SP) as security. Borrowers receive loans by minting GRAI, a token designed to reduce price volatility. Loans can reach up to 90% - 99% of the collateral's value, depending on the type of collateral.
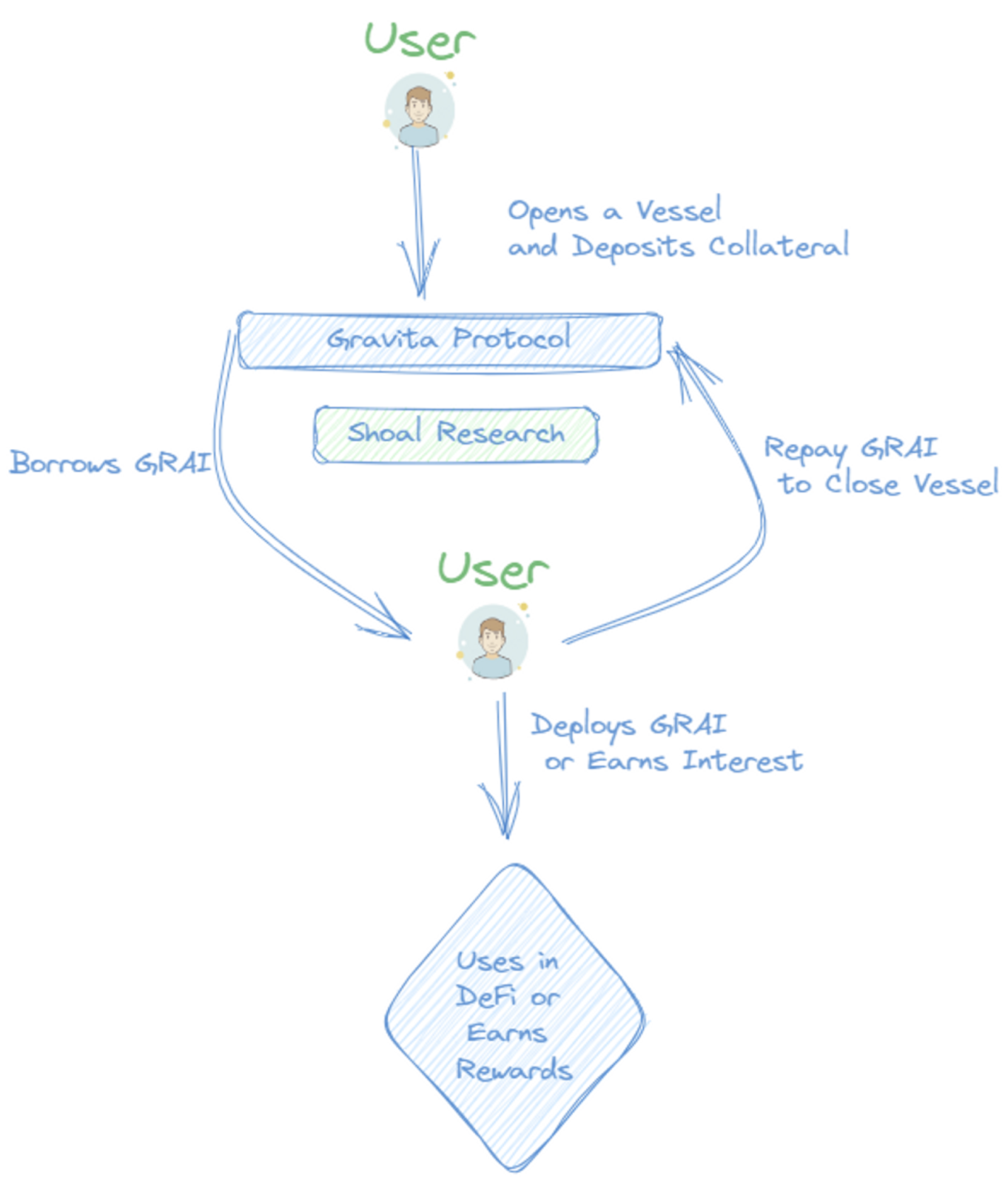
Here's how Gravita works:
Borrow GRAI: Users open a vessel to deposit collateral. They can borrow GRAI with a maximum fee of 0.5% and enjoy 0% interest indefinitely.
Deploy GRAI: 1 GRAI is equivalent to $1. Users can swap or spend it however they like or deposit it in Gravita's Stability Pool to purchase WETH and LSTs at a discount.
Repay GRAI: Users can close their vessel and withdraw collateral conveniently. Repaying within 6 months grants a partial refund of the 0.5% fee.
Earning Money with Gravita
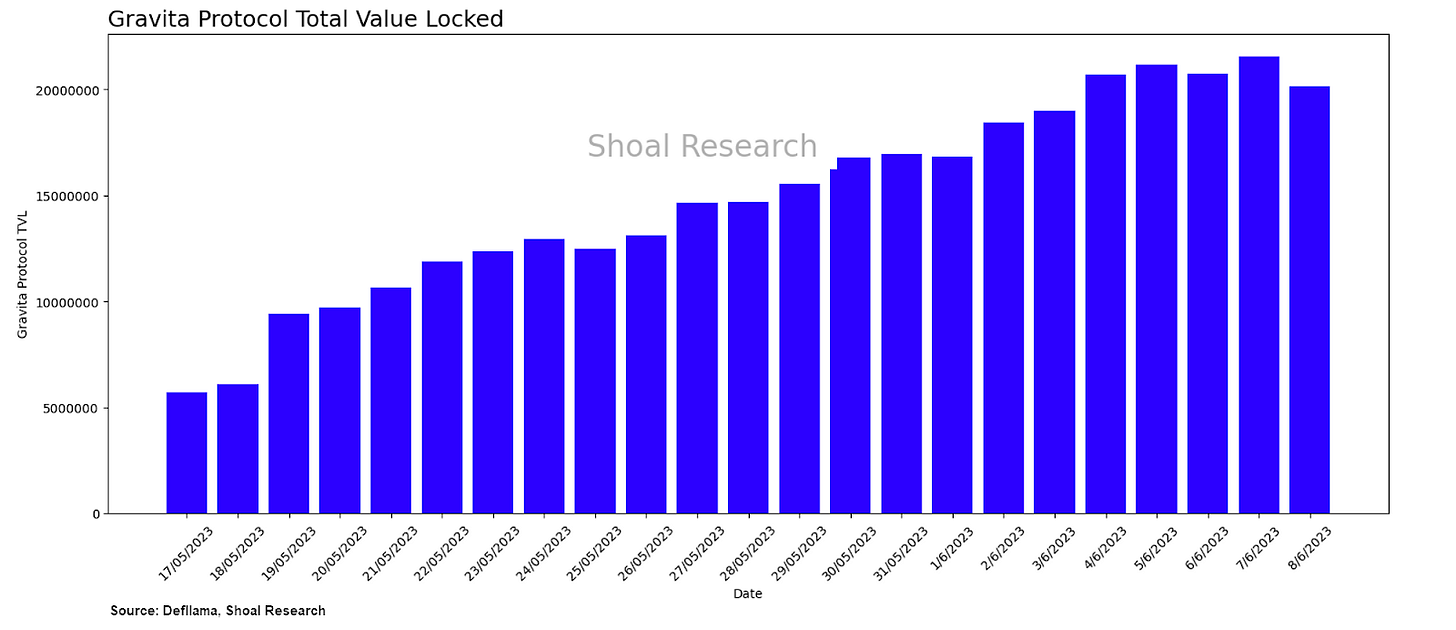
You can generate income on Gravita by contributing to the stability pool, designed to repay the debts of liquidated positions that exceed the maximum loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. You can earn income from liquidation gains by participating in the stability pool. Gravita may also introduce a governance token in the future to offer additional benefits to users. At the time of writing, the total value locked in the Gravita Protocol stands at around $20.6 million, up 10% weekly since launch. The protocol continues to attract more users as the TVL continues to grow.
GRAI and GRVT (soon) Tokens
GRAI is an over-collateralized debt token issued by Gravita, meaning that the collateral backing it exceeds the loan's value. It is generated when assets are deposited into the Gravita Protocol. The price of GRAI is kept within a certain range through mechanisms that establish a rigid price ceiling and floor, offering arbitrage opportunities that aid in maintaining price stability. Additionally, Gravita may launch a governance token named GRVT in the future to confer extra perks to users.
Pros
Interest-Free Loans
Diverse Collateral Types
Earning Opportunities
Non-Custodial and Transparent: Price Stability Mechanisms
Risks
Risk of Asset Loss
Dependence on User Understanding
Smart Contract Risk
Dinero Protocol
The Dinero Protocol is a decentralized finance (DeFi) project developed by the Redacted Cartel. It introduces a new permissionless stablecoin, Dinero, which is backed by user-owned block space and is designed to maintain a 1:1 value ratio with the US dollar.
Here's how Dinero works:
Stake ETH: Users with Ether can utilize the Dinero Protocol to stake their ETH.
Access a Premium Decentralized Remote Procedure Call (RPC): This feature revolves around DINERO as a medium of exchange.
ETH Liquid Staking Token (LST): The protocol includes an ETH liquid staking token (LST), which benefits from staking yield, and the Dinero Protocol.
Staking ETH: Empowering Users
Initially, DINERO will function like a typical collateralized debt position (CDP) stablecoin, such as $DAI. However, the ultimate goal is to use the underlying $ETH collateral to enable a decentralized RPC and a block builder that protects Dinero users from MEV attacks.
Decentralized RPC:
Dinero Protocol aims to democratize access to premium block space on the Ethereum network by allowing users to back their own block space and access a premium decentralized RPC. This unique feature opens up various possibilities, enabling users to interact with decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts with enhanced capabilities and efficiency.
ETH Liquid Staking Token (LST): Maximizing Benefits
Dinero Protocol introduces the ETH Liquid Staking Token (LST) to maximize user benefits. Users can earn staking yields from their ETH holdings by participating in the protocol while utilizing the Dinero protocol's additional utility. The LST acts as a bridge between the staked ETH and the Dinero ecosystem, providing users other benefits and opportunities within the protocol.
The Significance of Redaction and Curve:
The partnership between Redacted (the team behind Dinero) and Curve holds significant importance. In the early years of on-chain CDPs, achieving liquidity escape velocity was a primary challenge. The 'bribe power' associated with Redacted, in collaboration with Curve, plays a crucial role in addressing this challenge. Simply put, by utilizing curve protocol, Dinero can achieve critical mass liquidity to operate efficiently. These strategic alliances enhance liquidity and foster the growth and adoption of the Dinero Protocol within the DeFi space.
More Notable LSTfi CDPs
Origin Protocol: Origin Protocol is a platform that aims to bring the next 100 million users to crypto through its products in the NFT and DeFi sectors. Its Origin Token (OGN) stakers earn their share of Story's platform fees, and it also offers a yield-generating stablecoin called Origin Dollar (OUSD)
Tenet: Tenet is an EVM-compatible Layer-1 blockchain that utilizes liquid staking derivatives (LSDs) as collateral for network validators, enhancing security and governance inclusivity. It issues tLSDs, representing staked LSDs, and provides yield opportunities from multiple sources, including block rewards, dAPP user incentives, and its native stablecoin, LSDC, minted against overcollateralized positions of tLSDs.
Aave GHO: GHO is a stablecoin issued by Aave, and its value is pegged to the US dollar (USD). GHO is fully decentralized and secured by an over-collateralization mechanism, similar to Aave's crypto loans. Aave mints GHO tokens when users of its loan service deposit cryptocurrency as collateral to borrow GHO tokens.
Frax Finance: Frax Finance is a fractional-algorithmic stablecoin protocol that uses collateralization and algorithmic mechanics processes to create its decentralized stablecoin, FRAX. The collateral ratio, which is the ratio of collateral needed to back $1 of FRAX, varies with time and is solely determined by market forces. Only stablecoins are currently accepted as collateral by the protocol, with plans to accept more volatile collateral like wrapped BTC as the protocol is increasingly adopted
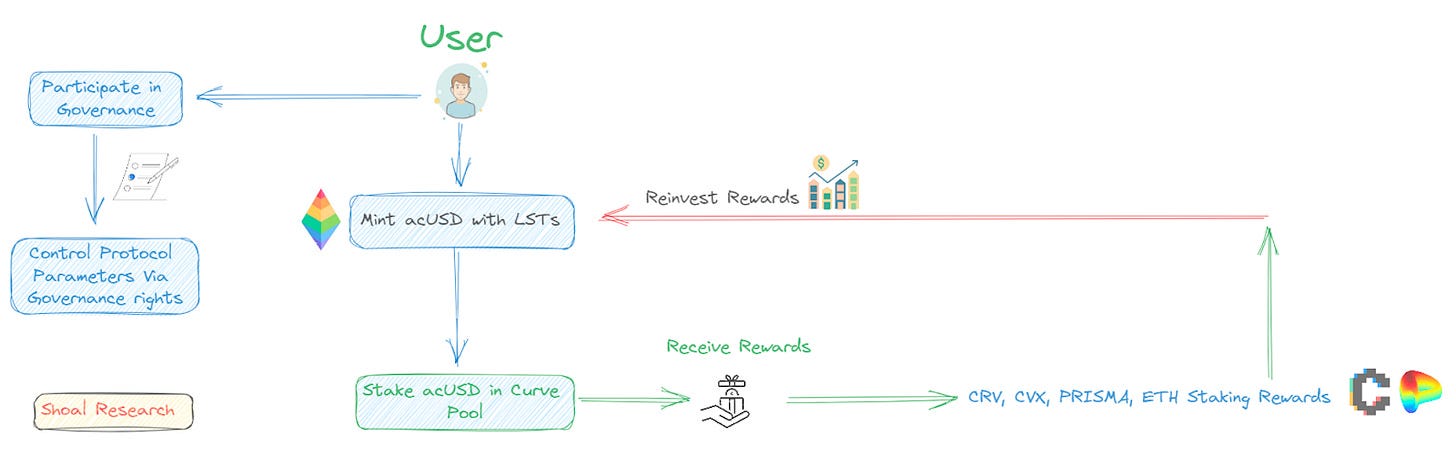
Prisma Finance: Prisma Finance is a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol that facilitates the utilization of LST as collateral for the purpose of borrowing acUSD, a stablecoin that is fully backed by collateral within the protocol itself. The act of staking acUSD on Curve and Convex platforms is met with rewards in the form of various incentives, including trading fees as well as the governance tokens known as CRV, CVX, and PRISMA.
Conclusion
In short, liquid staking derivatives finance (LSTfi) and collateralized debt positions (CDPs) are revolutionizing decentralized finance (DeFi) by allowing users the ability to leverage their assets, earn interest, and access DeFi services. These protocols provide innovative features such as stablecoin rebalancing, interest-bearing tokens, and unique collateral options. With a growing market and increasing value, LSTfi and CDPs are reshaping the DeFi landscape, creating new user opportunities.
LSTfi and CDPs are transforming DeFi by enabling asset leverage, interest earnings, and access to services. Notable protocols include crvUSD for stablecoin rebalancing, Lybra for interest-bearing stablecoins, Raft for unique leverage and flash mints, Gravita for borrower-friendly terms, and Dinero for user-owned blockspace and premium access. These protocols drive innovation in a rapidly evolving DeFi landscape.
Sources:
Not financial or tax advice. The purpose of this newsletter is purely educational and should not be considered as investment advice, a request to buy or sell any assets, or a suggestion to make any financial decisions. It is not a substitute for tax advice. Please consult with your accountant and conduct your own research.
Disclosure. All of my posts are my own, not the views of my employer.